Artificial Reality System Architecture For Concurrent Application Execution And Collaborative 3d Scene Rendering
US20250131636
2025-04-24
Physics
G06T15/005
Inventors:
Applicant:
Drawings (4 of 13)
Smart overview of the Invention
The patent application outlines a distributed, pluggable architecture for artificial reality (AR) systems, enabling the simultaneous execution and collaborative rendering of multiple AR applications. This system utilizes an image capture device to gather data from the physical environment and a head-mounted display (HMD) to present AR content. A concurrent application engine manages the rendering of this content, creating a unified scene that integrates objects from various AR applications.
Technical Field
The disclosure pertains to artificial reality systems, including virtual reality, mixed reality, and augmented reality. These systems are increasingly prevalent across diverse sectors such as gaming, education, and industrial applications. Typically, AR systems involve devices like HMDs to deliver user experiences by combining generated content with real-world visuals. The innovation focuses on allowing multiple AR applications to operate concurrently without the need for users to switch between them.
System Architecture
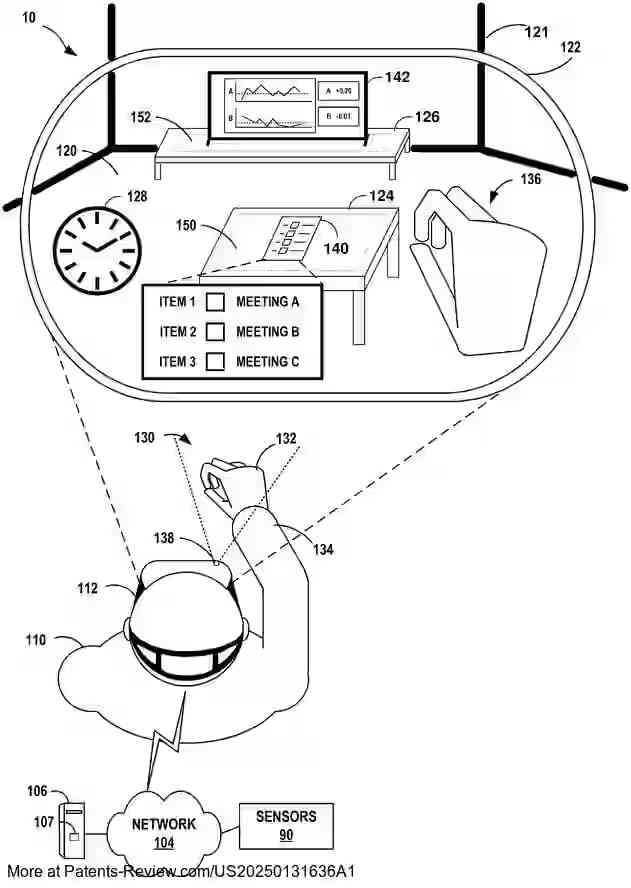
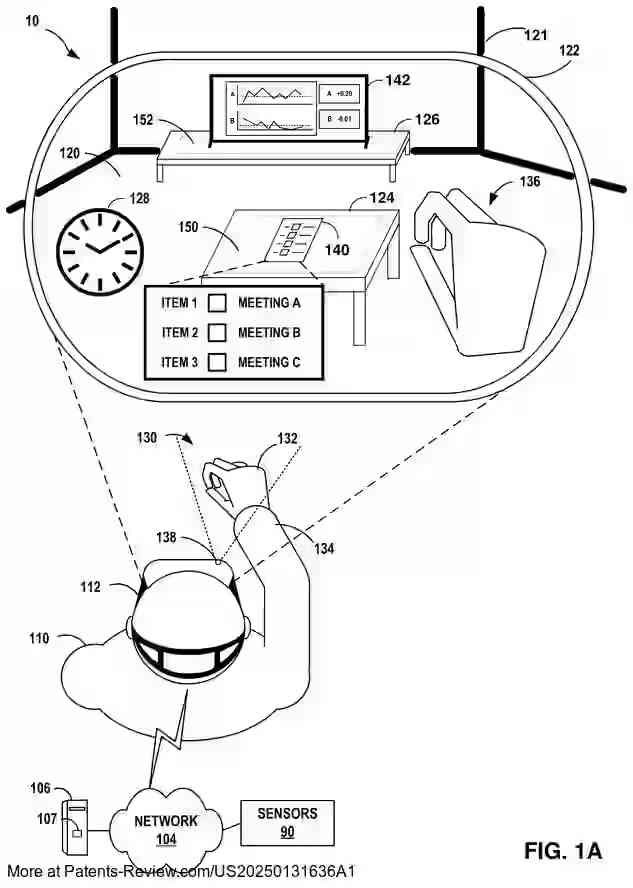
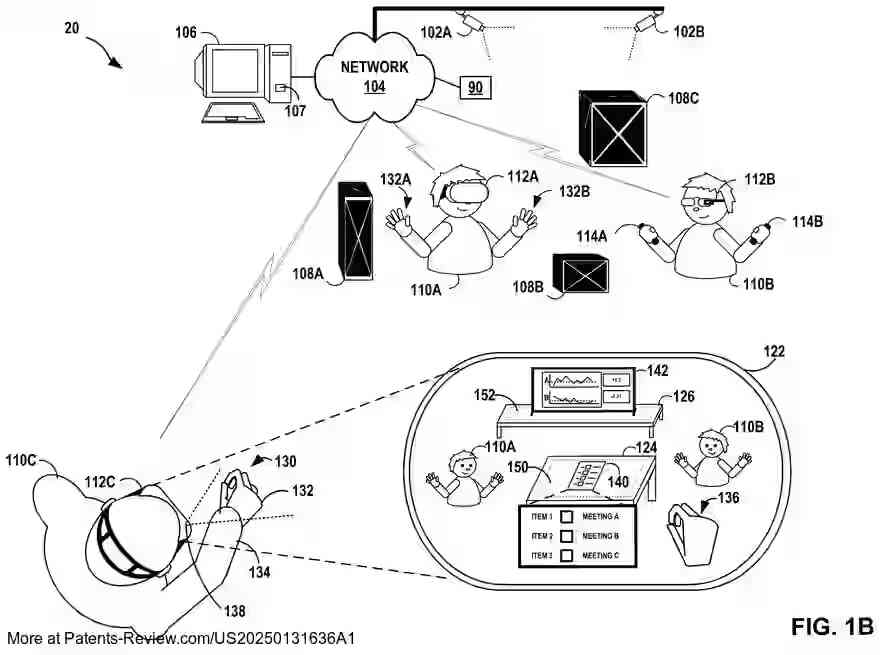
The architecture features a concurrent application engine with a centralized scene controller, or "shell," that provides an interface for AR applications to register and communicate 3D modeling information. This shell aggregates data from each application to position objects within a common scene and render them collectively. The system supports dynamic updates through a serialization protocol, enabling real-time interaction and manipulation by users while maintaining a seamless experience across multiple applications.
Functionality and Interaction
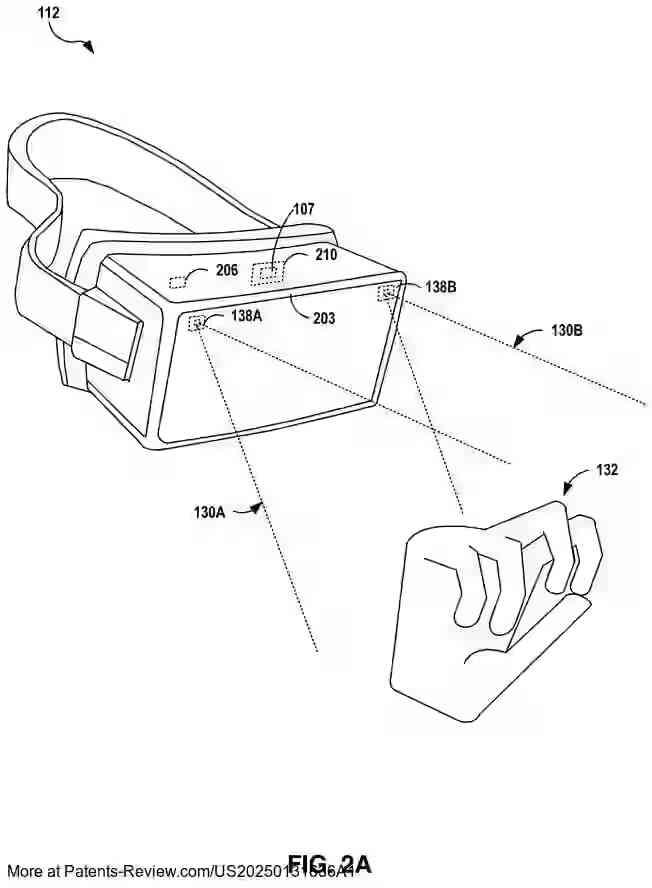
AR applications can specify global scene attributes and model their objects using the client interface, which includes functions for defining surfaces ("offer areas") and connections ("attachments") between these surfaces and objects. The centralized scene controller manages these interactions by constraining objects within predefined volumes ("containers"), ensuring proper placement and rendering within the scene. This approach allows for collaborative control over the rendered environment by multiple applications.
Advantages and Implementation
This architecture provides several technical benefits, such as multitasking capabilities in AR environments and improved resource management by shifting rendering control to the backend shell. The shell determines suitable object placements within scenes, allowing for efficient scene graph composition. By enforcing quality-of-service constraints, the system optimizes performance and resource use. The patent also describes methods for receiving, aggregating, and rendering modeling information from AR applications, enhancing user experience through seamless integration of diverse content.