DYNAMIC PUSH-PULL LENSES FOR XR DISPLAYS
US20250138320
2025-05-01
Physics
G02B27/0172
Inventors:
Applicant:
Drawings (4 of 19)
Smart overview of the Invention
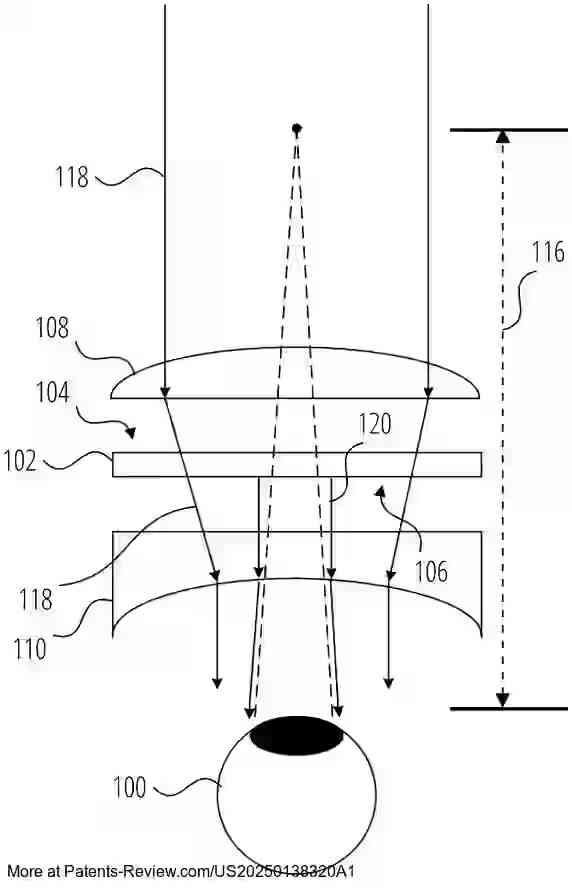
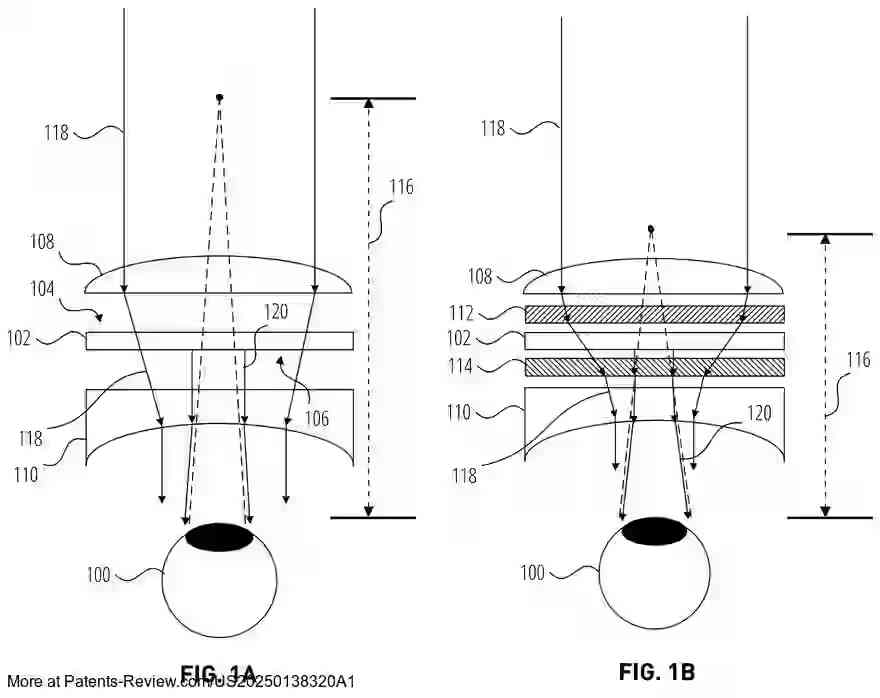
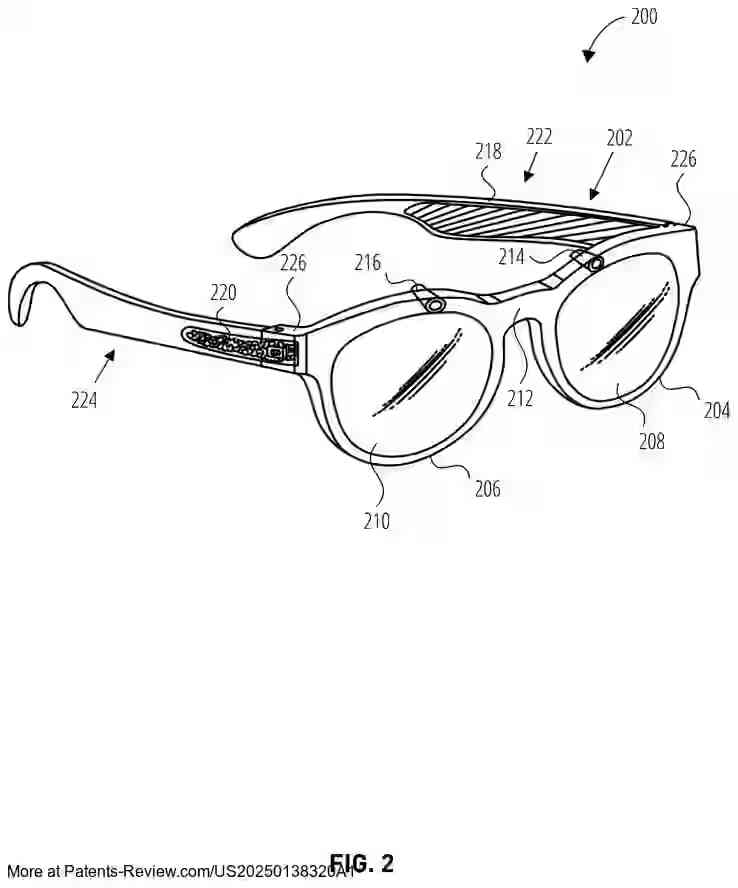
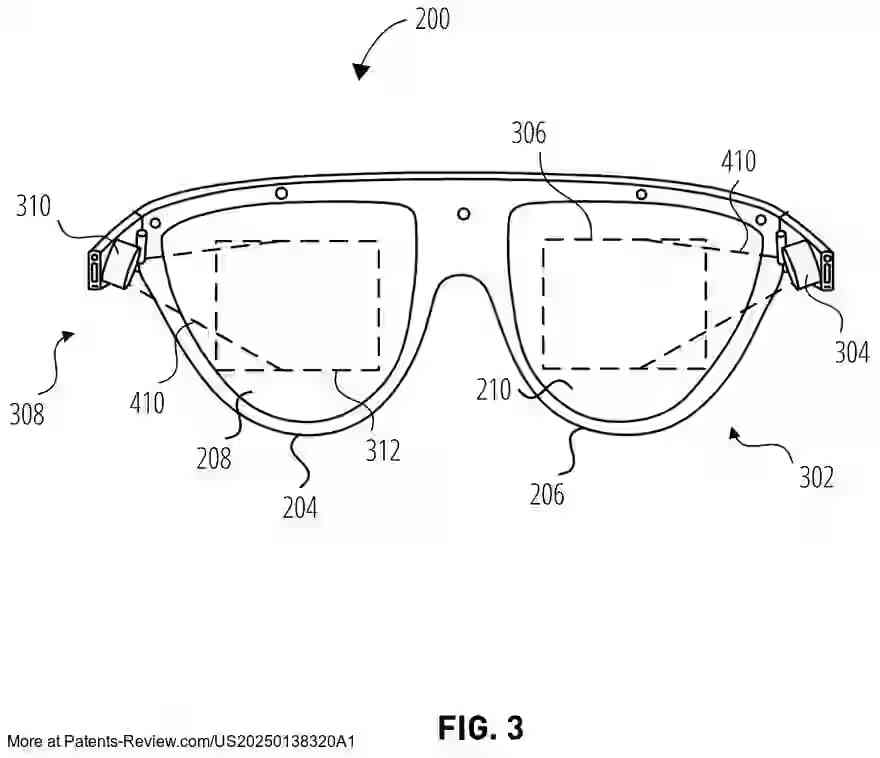
The patent application discusses an extended reality (XR) display system that incorporates dynamic push-pull lenses to enhance the realism and comfort of virtual content presentation. The XR display includes a near-eye optical see-through component, which presents virtual images to the user's eye through a combination of a dynamic push lens on the world-facing side and a dynamic pull lens on the eye-facing side. These lenses utilize liquid crystal cells that can switch between active and inactive states, applying positive or negative optical power to converge or diverge light respectively.
The primary challenge addressed by these lenses is the distortion of real-world and virtual images. The push lens converges environmental light before it reaches the image presentation component, ensuring that real-world visuals remain undistorted. Simultaneously, the pull lens diverges light as it exits towards the user's eye, making virtual content appear closer than it would naturally be perceived, thus resolving the issue of infinite focal distance common in many XR systems.
Dynamic lenses offer the ability to adjust both focal and vergence distances dynamically, which is crucial for maintaining visual comfort and realism. By presenting virtual content at varying depths, these lenses prevent discomfort caused by mismatches between vergence and focal distances. The system can switch between different optical power states to present virtual content at varying depths, enhancing user experience by allowing objects to appear at more natural distances.
The implementation of these dynamic lenses involves liquid crystal technology controlled by ring electrodes, which adjust the refractive index across the lens surface. This adjustment allows the dynamic push lens to function like a convex or Fresnel lens and the pull lens like a concave lens. Such configuration enables precise control over how light is manipulated as it passes through the lenses, thereby improving both the clarity and depth perception of virtual content.
In conclusion, this technology addresses several technical challenges in XR systems by providing a mechanism for dynamically adjusting focal distances without compromising real-world visual clarity. It enhances user comfort and realism in XR experiences by allowing seamless integration of virtual content into the user's real-world field of view, expanding the potential applications of XR technologies across various fields.