VIDEO ASSEMBLY USING GENERATIVE ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
US20250140291
2025-05-01
Physics
G11B27/031
Inventors:
Applicant:
Drawings (4 of 30)

Smart overview of the Invention
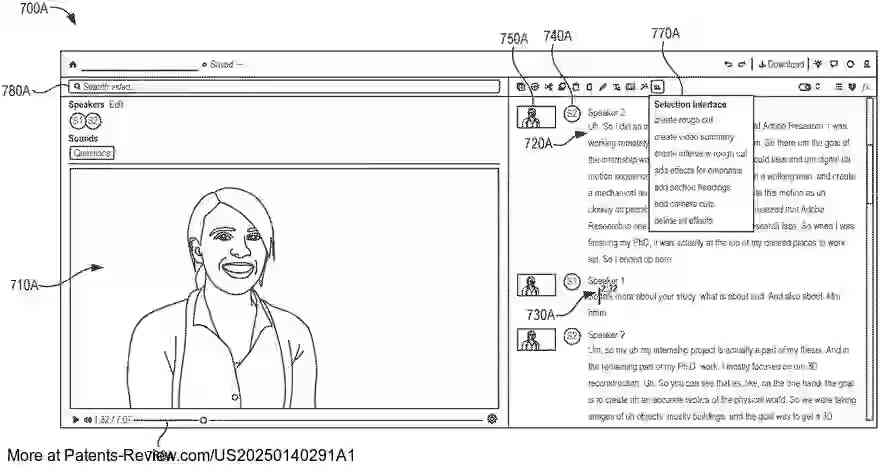
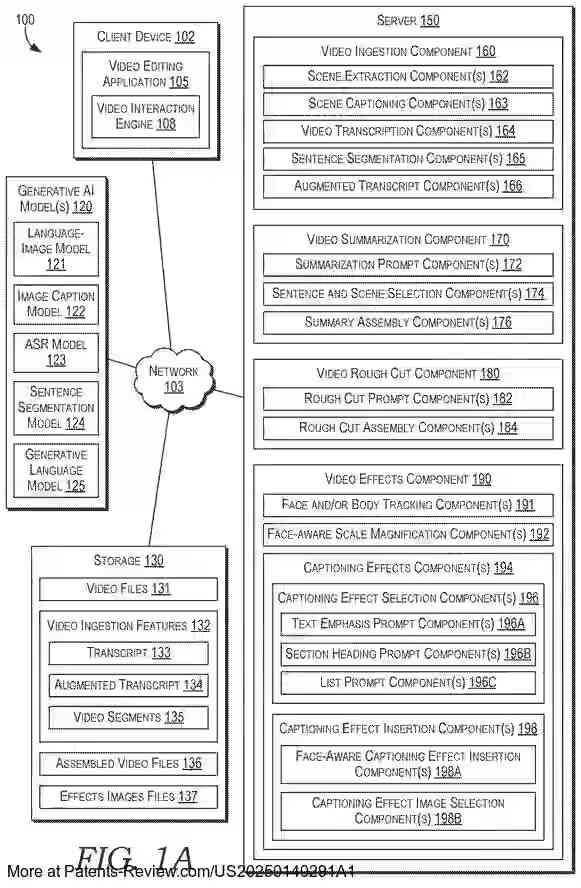
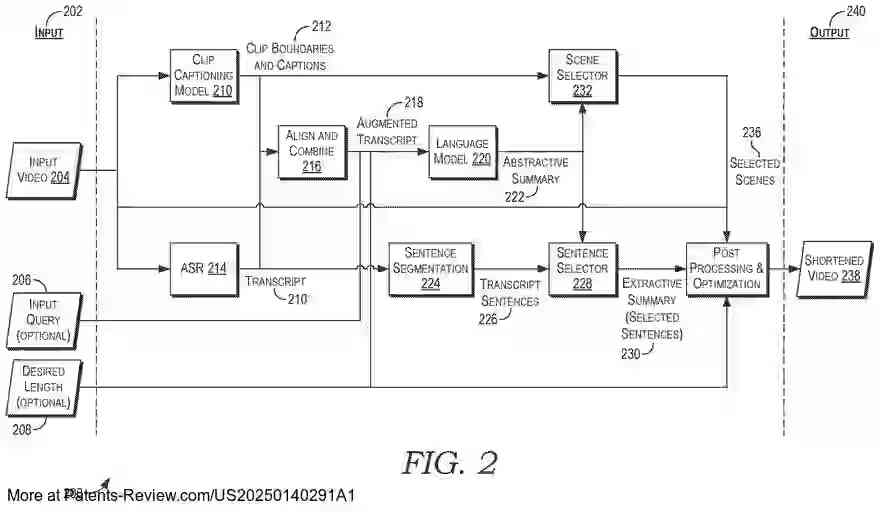
The invention leverages generative artificial intelligence to streamline video editing by identifying and assembling key segments of a larger input video into smaller, trimmed versions. This process involves extracting visual scenes and captions, which are then matched with diarized and timestamped transcripts to create an augmented transcript. This augmented transcript is processed by a large language model to generate a natural language summary, which helps identify corresponding video segments for assembly into trimmed videos. These trimmed versions can be customized based on user queries or desired lengths.
Background
With the rise in video usage across various industries, there is a growing need for efficient video editing tools. Traditional video editing requires manual selection and editing of frames, which can be tedious and time-consuming, often exceeding the skill level of many users. As technology advances, there is an increasing demand for automated solutions to simplify this process and make it more accessible to novices.
Summary
The technology provides methods for using AI to automatically edit videos by focusing on significant segments and applying relevant effects. It identifies important parts of a video using scene extraction and transcription techniques, allowing for the generation of shorter, more focused videos. The system can apply effects such as face-aware scale magnification to smooth transitions between segments and add captioning effects to highlight key points within the video.
Detailed Description
Conventional video editing interfaces rely on manual frame selection, which is slow and labor-intensive. This invention reduces computational resources by automating the editing process through AI, minimizing the need for manual input. By utilizing AI, the system can efficiently process large videos, reducing network latency and computational costs associated with traditional methods.
Implementation
The system accesses user-designated input videos through a video editing application, allowing users to specify options for creating trimmed versions. Users can select the desired length or provide queries to focus on specific topics or storylines. The application extracts visual scenes with start and end times using a language-image pretrained model, clustering frames based on similarity to determine scene boundaries.